Press release -
Discovered “GT-7” compound induces cell death in pancreatic cancer cells - Expected for a new treatment approach different from the mechanisms of conventional anticancer drugs
A research team led by Prof. Reiko Sugiura of Kindai University (Higashi-Osaka city), Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacogenomics, Faculty of Pharmacy, found that a compound called "ACAGT-007a" (GT-7*1) strongly reduces the viability of pancreatic cancer cells with specific gene mutations and induces cell death (apoptosis*2). The team also found that GT-7-mediated apoptosis can be enhanced in combination with certain types of inhibitors that prevent the enzyme's aberrant activation and cell proliferation. The findings of this research will help find a novel therapeutic approach different from the conventional mechanisms of anti-cancer drugs, thus a new application is highly anticipated. This research was published in "Cells", an international life-science journal on Thursday, February 17, 2022 (10:00 am, Japan time).
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/4/702
[Key points]
- Found that GT-7 induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells with specific gene mutations.
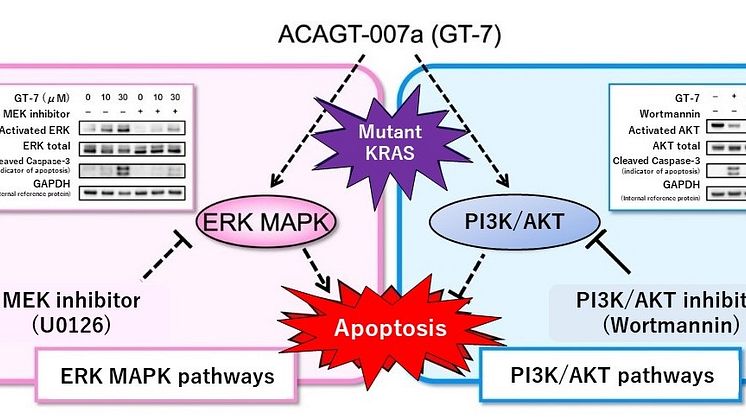
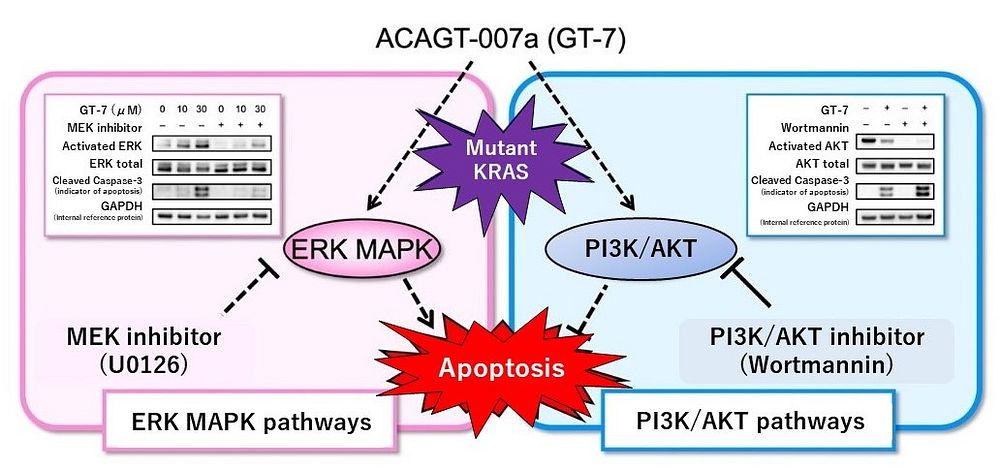
- GT-7 induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells by promoting abnormal activation of an enzyme called "ERK MAPK" ("ERK") *3.
- Expected for new treatment methods for pancreatic cancer using an inhibitor of the enzyme called "PI3K/AKT" ("AKT") *4 in combination with GT-7.
[Background]
Signaling pathways with various proteins play an important role in cell proliferation and cell death and regulate cell turnover normally. When a protein gene is mutated, cell death is not properly induced, causing unregulated proliferation of cancer cells.
In more than 90% of pancreatic cancers, mutations in the KRAS gene cause abnormal activity of two enzymes, ERK and AKT, both of which promote cell proliferation. It is believed that this causes the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells. Many of the conventional anti-cancer drugs have suppressed the proliferation of cancer cells by inhibiting the ERK signaling pathway, but the therapeutic effect on pancreatic cancer is insufficient. It is necessary to develop a new therapeutic approach, using other mechanisms.
[Overview]
The research group led by the Faculty of Pharmacy, Kindai University focused on the abnormal activation of two enzymes, ERK and AKT, in pancreatic cancer cells with specific gene mutations. In this study, they examined if the compound GT-7, which induces apoptosis in ERK-active melanoma cell lines, is also effective for pancreatic cancer. The result showed that GT-7 strongly suppresses the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells and induces apoptosis by stimulating ERK activation aberrantly.
Many of the conventional therapeutic regimes inhibit ERK activation, whereas GT-7 induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer by a completely different mechanism. It was also revealed that the apoptosis-inducing effect of GT-7 is significantly enhanced when used in combination with a drug that inhibits AKT activation in pancreatic cancer cells. Based on the findings of this research, it is expected that the combined use of the GT-7 and AKT inhibitors will help develop a novel therapeutic approach for pancreatic cancers driven by mutations in the KRAS gene.
[About publication]
Journal name:
Cells(Impact factor: 6.6@2020)
Research paper title:
ACAGT-007a, an ERK MAPK Signaling Modulator, in Combination with AKT Signaling Inhibition Induces Apoptosis in KRAS Mutant Pancreatic Cancer T3M4 and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 Cells
Authors:
Golam Iftakhar Khandahar1, Ryosuke Satoh1、Teruki Takasaki1, Kana Fujitani1, Genzoh Tanabe1、Kazuko Sakai2, Kazuto Nishio2, Reiko Sugiura1*
(* Correspondence author)
Affiliations:
1 Faculty of Pharmacy, Kindai University
2 Faculty of Medicine, Kindai University
[Glossary]
*1 ACAGT-007a (GT-7): Aiming to develop a compound that regulates MAPK activity, this compound was identified by a research group at the Faculty of Pharmacy, Kindai University, using a unique drug development approach with fission yeast that has signal transduction molecules similar to that of humans. ACAGT-007a (GT-7) selectively induces apoptosis in melanoma cell lines.
*2 Cell death (Apoptosis): Regulated cell suicide process or programmed cell death. When a tadpole transforms into a frog, the tail is removed through apoptosis. Many of the anticancer agents used clinically have the effect of killing cancerous cells by inducing apoptosis.
*3: ERK MAPK (ERK): One of the kinases (phosphorylating enzymes) associated with signaling for promoting cell proliferation. ERK MAPK is abnormally activated in certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer and melanoma, and plays an important role in cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Activated RAS chain reaction leads to ERK activation.
*4 PI3K/AKT (AKT): This is a serine /threonine kinase associated with controlling various functions such as cell proliferation, metabolism, and protein synthesis. Upon external stimulation, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is activated, and the produced PI3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) activates AKT.
*5 KRAS: One of the RAS protein family (KRAS, HRAS, and NRAS) associated with signaling that promotes cell proliferation. If any of the genes encoding the KRAS protein is mutated, an abnormal KRAS protein is produced, and ERK signaling pathways and AKT signaling pathways that promote cell proliferation are constantly activated. It is believed this causes cancer.
*6 Melanoma: Malignant melanoma. This is a cancerous form of "melanocytes (normal pigment cells)," cells that produce melanin, which is a pigment component of spots and moles. One of the cancers that metastasize early and has the highest malignancy and mortality rate.