Press release -
Elucidation of the role of "Stress Granules" that can be therapeutic targets for cancer and ALS -- Kindai University
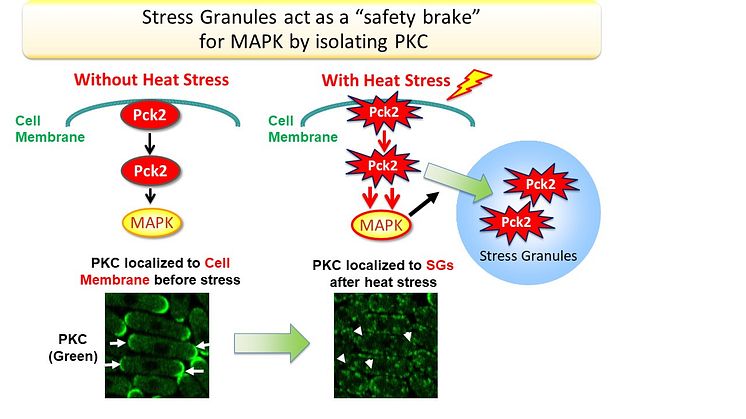
- Discovered for the first time in the world that Stress Granules (SGs) have the role of a "safety brake" that regulates signaling pathways that control cell proliferation, such as Protein Kinase C (PKC) and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK).
- SGs have the function of preventing excessive activation of MAPK by incorporating PKC.
- Suggests that controlling SGs may lead to treatment of diseases such as cancer and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).
Higashiosaka, Osaka, Japan. January 26th, 2021
A research group led by Prof. Reiko Sugiura, the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy, Kindai University (Higashi-Osaka, Osaka), found that stress granules (SGs) are non-membranous cytoplasmic dots that form when cells are stressed. SG assembly is a cellular strategy to cope with stress-related damage.
Notably, cancer cells also utilize SGs to maintain their growth. For the first time in the world, the group discovered that SGs have the role of a "safety brake" that controls proliferation signals such as Protein Kinase C (PKC) and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK). In recent years, SGs have attracted a great deal of attention as a therapeutic target for various cancers and intractable neurological diseases such as ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis). The results of this study show that controlling SGs may lead to the treatment of diseases caused by excessive activation of "PKC" and "MAPK".
The research paper is available online in the American life science magazine "Journal of Cell Science" on January 26, 2021, 21:00 (Japan Standard Time).
https://jcs.biologists.org/content/134/2/jcs250191
About Publication
Research paper title: Sequestration of the PKC ortholog Pck2 in stress granules as a feedback mechanism of MAPK signaling in fission yeast
Journal name: Journal of Cell Science(Impact factor: 4.573)
Authors: Yuki Kanda, Ryosuke Satoh, Teruaki Takasaki, Naofumi Tomimoto, Kiko Tsuchiya, Chun An Tsai, Taemi Tanaka, Shu Kyomoto, Kozo Hamada, Toshinobu Fujiwara, Reiko Sugiura
For media enquiries, please contact koho@kindai.ac.jp , Public Relations Department, Kindai University.
